[Thorough explanation! ] What is the distribution and cold chain that maintains the quality of frozen foods?

If you handle perishable foods such as fresh produce, you may have wondered how to deliver them to consumers without sacrificing quality.
This time, we will explain the ``cold chain,'' a system that distributes products while keeping them at a consistently low temperature from the place of production to the place of consumption.
We have summarized the meaning of cold chain, market size, development status in Japan and overseas, etc. based mainly on the ``2013 Cold Chain Survey in Major Countries and Regions'' prepared by JETRO.
This is a must-see for those who want to deliver food to consumers in high quality through refrigerated or frozen delivery!
目次
What is cold chain?

Meaning of cold chain
Cold chain refers to a system in which products are distributed at consistently low temperatures from the point of production to the point of consumption. It is used to transport perishable foods, medicines, electronic parts, etc. that need to be kept refrigerated or frozen.
Benefits of cold chain
When transporting fresh food, switching from room-temperature distribution to low-temperature distribution will significantly extend the freshness period. Extending the freshness retention period has various benefits, such as reducing waste loss during the distribution stage, allowing products to reach consumers while remaining fresh, and making it possible to export them overseas.
Cold chain market size
Demand for frozen and chilled foods is increasing both domestically and overseas. Along with this, cold chains are being developed and the market size is expanding.
According to the American research firm Report Ocean, the global cold chain market size will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.7% over the forecast period from 2022 to 2030, and reach 79.27 billion by 2030. It is predicted to reach USD. Along with this, the domestic cold chain has also been maintained at a high level.
Additionally, the cold chain market is rapidly expanding overseas, especially in East Asia.
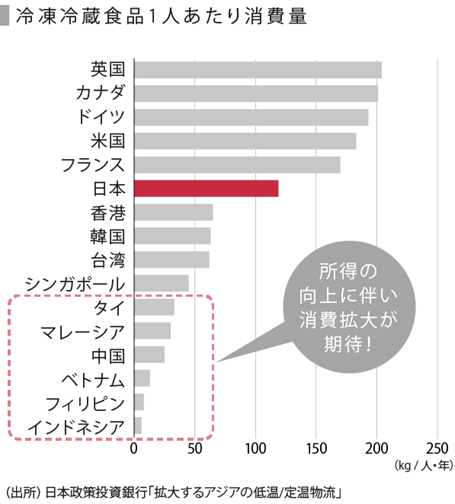
This figure shows that consumption of frozen and refrigerated foods in East Asia is still lower than in developed countries.
In the future, with economic development, the demand for frozen and refrigerated foods is expected to rapidly expand, and the development of cold chains will continue to advance.
For this reason, it is believed that there is room for Japanese-style logistics to enter the market, and in March 2021, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism formulated the "Dissemination Strategy for Japanese-style Cold Chain Logistics Service Standards in ASEAN" and promoted the Japanese cold chain. We are starting efforts to popularize it.
cold chain system
The cold chain is divided into production/processing, distribution, and consumption stages. We will explain what kind of mechanism is required for each.
Production/processing

In the case of distributing vegetables and fruits, this applies to the harvest area, and in the case of processed foods such as frozen foods, it corresponds to the processing factory.
When fruits and vegetables are distributed raw, the first step in the cold chain is pre-cooling.
Pre-cooling refers to the low-temperature treatment performed on fruits and vegetables before shipping. Lowering the temperature of fruits and vegetables reduces the amount of respiration, which greatly changes the quality of the fruits and vegetables.
After the fruits and vegetables have been pre-cooled, they are stored in a high-freshness refrigerator until shipped.
Normal refrigerators dry out food, but high-freshness refrigerators have various ways to maintain freshness, such as increasing humidity.
Additionally, if raw meat, raw fish, or processed foods are to be frozen and distributed, they must be frozen first.
At this time, the key is to freeze the food at a higher quality. When food is frozen, ice crystals destroy the cells and reduce the quality of the food.
Even if the temperature after freezing is properly controlled, if the quality deteriorates during freezing, it will reach the consumer with that low quality.
For this reason, it is now common for frozen foods to be rapid freezing, which does not damage the food's cells.
>>Click here for a detailed explanation of rapid freezing that does not reduce food quality.
In addition, businesses seeking even higher quality refrigeration are introducing special rapid freezer combine quick rapid freezer with electromagnetic wave mechanisms.
distribution

It is a very important stage that connects production to consumption.
At the distribution stage of the cold chain, food is transported by freezer/refrigerated trucks and temporarily stored in refrigerated/refrigerated warehouses. This also includes refrigerated warehouses for long-term storage for the purpose of stable supply, and frozen and refrigerated warehouses for temporary wholesale storage.
Low-temperature transportation is more expensive than normal-temperature transportation, but in Japan, thanks to various innovations by major distribution companies, it is possible to transport products at almost the same price as normal-temperature transportation.
However, when exporting food overseas, it is necessary to understand not only domestic distribution but also overseas distribution. Particularly in East Asia, there are many cases where refrigerated transportation is not well established, so care must be taken.
consumption

The cold chain at the consumption stage consists of refrigerators for commercial use such as restaurants and refrigerators for general households.
Many modern refrigerators have advanced features such as chilled and partial storage, making it easier to maintain freshness even during consumption.
Cold chain challenges

Consistent temperature control required
In order to deliver high-quality food to consumers, thorough temperature control is required at all stages of production, processing, distribution, and consumption.
If any one of these is not managed well, it will be impossible to deliver high-quality products to consumers.
Furthermore, there are some areas where it cannot be said that a completely consistent cold chain has been established within Japan.
For example, there are problems such as fruits and vegetables not being properly pre-cooled before being shipped, or being left out in the open at room temperature at wholesale markets.
As the temperature rises, the amount of respiration of fruits and vegetables increases, leading to rapid deterioration. If you are shipping a product, we recommend that you check the route through which it is being distributed.
Building a cold chain is expensive
Cold chains are costly because they require all aspects of production, processing, distribution, and consumption to be in place.
Large-scale frozen and refrigerated warehouses are often required at the distribution stage, so building your own cold chain would be difficult unless you are a major food chain store.
In addition, overseas countries need to establish social infrastructure such as roads, electrical infrastructure, and the widespread use of refrigerators, so it will take not only money but also time for cold chains to become widespread.
Overseas cold chain

china cold chain
China's cold chain market has grown by more than 20% annually from 2015 to 2020.
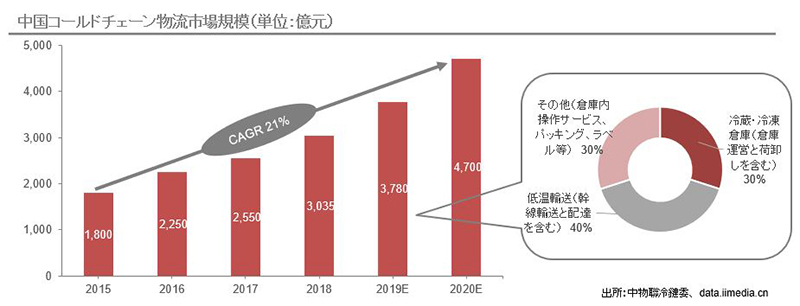
However, the consumption of frozen and refrigerated foods is still low compared to developed countries, so the frozen and refrigerated food market is expected to continue expanding in the future.
In response to such demand, construction of expressways to inland areas and the construction of frozen and refrigerated warehouses are underway.
The "Agricultural Products Cold Chain Logistics Development Plan" was announced in 2010, and cold chain logistics has been rapidly developed. I need to find out.
As cold chains have been developed in urban areas such as Shanghai, frozen and refrigerated foods are now being handled not only by Japanese retailers but also by high-end foreign supermarkets and local supermarkets.
However, when it comes to exports from Japan, there are only a limited number of foods that can be stored in refrigeration, and the majority are frozen foods.
Most refrigerated foods include dairy products and meat produced in China.
The reason why there are so few refrigerated foods exported from Japan is that it is extremely difficult to transport them from Japan to local stores while maintaining the refrigerated temperature range, and to avoid the risk of not selling out before the expiration date. You can
cold chain in india
According to Indian research firm 'Mordor Intelligence', the cold chain industry across India is expected to grow at an annual growth rate of over 14% during the forecast period of 2020-2025.
Although the cold chain, especially in urban areas, has developed to a high level, 40% of India's annual agricultural products are wasted, and the cold storage capacity is only 3,011 tons compared to the required 6,100 tons. Considering that there is no such thing as a cold chain market, it is expected that the cold chain market in India will continue to develop rapidly in the future.
Complaints about food deterioration in the frozen category account for less than 1%, and if the product is found to be damaged, it is returned to the delivery company or wholesaler.
While cold chains are in place in major cities, services at the national level are still under development because many companies only operate refrigerated and frozen delivery businesses in limited areas.
Therefore, it can be said that there are still many challenges in distributing refrigerated and frozen products throughout India.
Conclusion
Cold chain is a distribution method that you must know if you want to deliver food in high quality condition.
Especially for those exporting food overseas, check the cold chain situation in the area where the consumers are located.
We recommend that you investigate further.
⇒⇒Reserve a test room where you can compare rapid freezer








![[Storage period increased by 30 times! ] Achieving a stable supply of raw whitebait!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/579c55e6d32e1385c250e8e7c3ed59a71.jpg)
![[Sales increased 100 times! ] rapid freezing the signature menu “Ni-katsu sandwich”!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/IMG_02391.jpg)
![[Horse sashimi] We have significantly reduced waste loss with rapid freezer!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/5fda59d0cbcdabde18e58c3c58c09ed0.jpg)




![[Storage period increased from 3 days to half a year! ] Restaurants are expanding their business using wholesale and mail order!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/66c19942ab4ba346fdb64ccc04cde373.png)
![[Reduce loss from 200 kg of oysters to zero] Improve loss and expand business with rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/19785ca583a8d3c4041c7c192d041b0d.jpg)
















![[Delicious frozen foods] How to use them in lunch boxes, dinners, and snacks](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/frozen-food-1024x683-1.jpg)
![[Instant cooling at -196℃] What's up with cooling equipment that uses liquid nitrogen?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/4b219d54bd662f10cbae6ea211f612dd.webp)




![[For maintaining food quality!] Three functions you should know about constant temperature and high humidity storage](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/krefrigerator.jpg)
![[How long does frozen fish and meat last? ] Interesting expiration dates and tips to extend the shelf life](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/f124221382987fe32d0ffda6b6f497c1.jpg)
![[Required for Cook Chill System] How much does a blast chiller cost?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/fc29ddca3d7d1f8d53bf99518ce28fcf.webp)


![[Eliminating the labor shortage! ] Introducing the benefits of the cook-freeze system!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/72352e99f79e7f2bfa6e9eca24acceb0.webp)





