What is the manufacturing process that maintains the safety of frozen foods? Explaining standards and actual procedures

The frozen food market is rapidly expanding due to the coronavirus pandemic. In addition, in recent years, it has become possible to enjoy the taste of Michelin-rated restaurants created by top chefs at home through frozen foods.
With the number of delicious frozen foods on the rise, some people may be thinking about selling their own dishes and foods frozen. In some cases, when freezing your own food products, you may be concerned about the loss of taste or quality.
In this article, we will first introduce the manufacturing process of frozen foods and the standards for frozen foods from the perspective of the manufacturing process. Then, in the second half, we will introduce the "rapid freezing" technology that is essential to the frozen food manufacturing process and the recommended rapid freezer "Artlock Freezer."
目次
Introducing the manufacturing process of frozen foods

First of all, there are three main definitions and standards for frozen foods:
- Standards for ingredient standards under the Food Sanitation Act
- Standards in the quality labeling standards of the Food Labeling Act
- Standards established by the Japan Frozen Foods Association
Many commercially available frozen foods comply with the following standards indicated in ③.
- Pre-treatment (removal of inedible parts, cooking, etc.)
- Be frozen quickly so that it quickly passes through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature range (approximately within 30 minutes)
- It must be placed in a container/package and have the specified labeling.
- Always stored at -18 degrees Celsius or below throughout every stage from manufacturing to sales.
In this chapter, we will take a closer look at the manufacturing process of frozen foods while comparing them with the above standards.
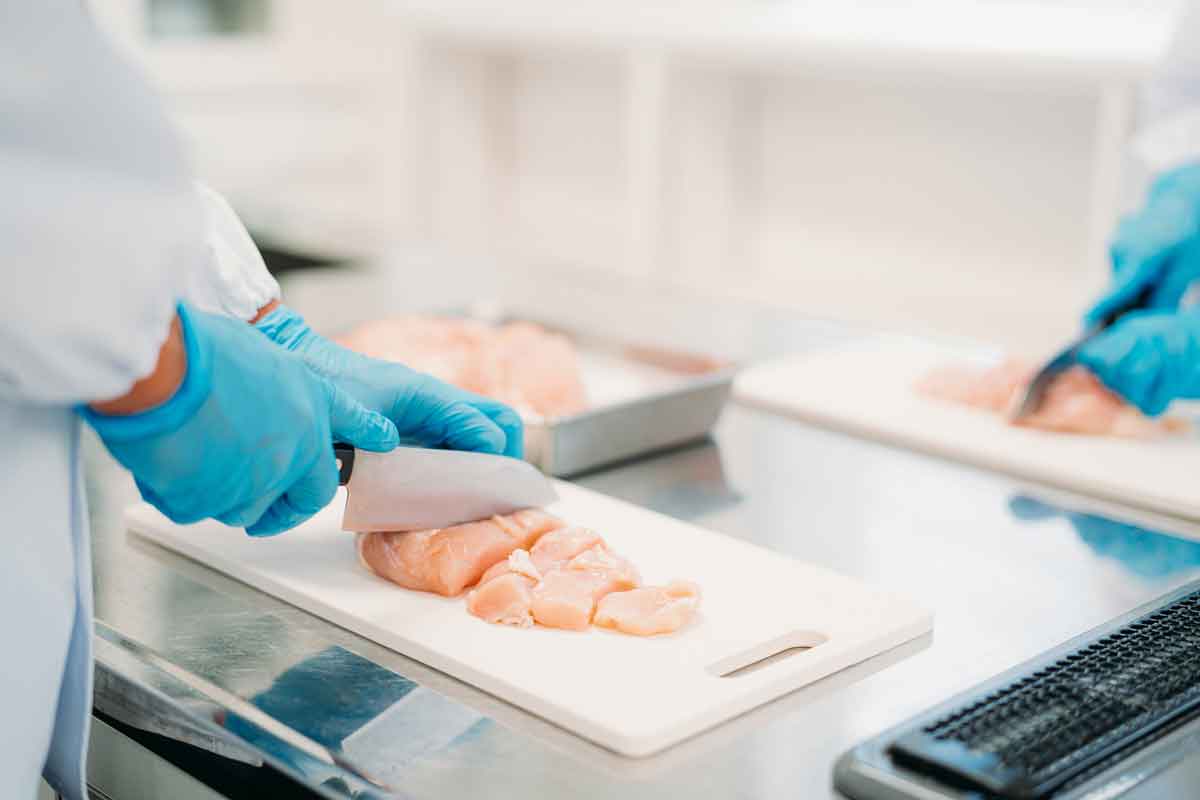
1.Food pretreatment/cooking
This process falls under the first of the four conditions for frozen foods: ``Pretreatment (removal of inedible parts, cooking, etc.) has been performed.''
When producing frozen foods, the ingredients are first pretreated. Preprocessing is a general term for the following operations that remove inedible parts from foodstuffs.
- Vegetables: wash and cut
- Fish: Peel off the scales, remove the internal organs and head, and cut into three pieces, etc.
By performing this pretreatment, there is no need to discard unnecessary parts in home kitchens or restaurant kitchens, and frozen foods can be used directly for cooking.
2. rapid freezing of food
This process applies to the second of the four conditions for frozen foods: ``The food must be rapidly frozen so that it quickly passes through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature range (approximately within 30 minutes).''
Ingredients and foods sold as frozen foods are frozen using a method called" rapid freezing "to maintain their quality. The characteristics of rapid freezing can be easily visualized by comparing it with so-called general freezing.
General freezing is like placing food outdoors in the extremely cold temperatures of Hokkaido, for example, and slowly freezing it at negative outside temperatures. On the other hand, rapid freezing is a freezing method that meets standards such as ``the food passes through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature range of -1 to -5 degrees Celsius within 30 minutes.'' .
Ice crystals will be kept small if the maximum ice crystal formation zone is passed within 30 minutes. As a result, there is less damage to food, which is a major advantage of rapid freezing.
3. Packaging frozen foods
This is a process that applies to the third of the four conditions for frozen foods: ``The food must be placed in a container or package and the specified labeling must be displayed.''
In order to maintain the quality of rapid freezing foods, it is necessary to take measures to prevent deterioration during the storage and distribution processes after production. Therefore, it is important not only to simply wrap and seal the food, but also to choose a packaging material that is suitable for the food and ingredients.
In addition, after frozen foods are packaged, they must be labeled with information such as product specifications, cooking methods, and ingredients. The combination of appropriate packaging that maintains food hygiene and information labeling is called "consumer packaging (commercial packaging)."
4. Store and distribute under temperature control
This process applies to the last of the four conditions for frozen foods: ``Through every stage from manufacturing to sales, the food must be stored at -18 degrees Celsius or below.''
After production of frozen foods, thorough temperature control is required in order to store and distribute them at -18 degrees Celsius or below. This -18 degrees is an international voluntary standard.
In contrast, Japan's Food Sanitation Law stipulates that the storage temperature for frozen foods is -15 degrees Celsius or lower. This -15 degrees was set because if the temperature dropped any further, microorganisms on Earth would no longer proliferate. In other words, if the temperature is below -15 degrees, frozen foods are less likely to spoil.
However, at -15 degrees, the taste and quality of frozen foods may change. For this reason, the frozen food industry has set a voluntary standard of -18 degrees Celsius or below based on the results of a U.S. survey.
Frozen food standards from the manufacturing process perspective

Frozen foods have standards for each manufacturing process. In this chapter, we will introduce the four standards and manufacturing process characteristics of frozen foods.
Frozen food consumed after heating
Frozen food that is eaten after being heated. This applies to foods that are heated in a microwave or hot water bath. It can be divided into two types depending on whether it was heated before freezing.
- Heating just before freezing: Food heated just before freezing
- Unheated just before freezing: Food that has not been heated just before freezing
In addition, at quarantine stations under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, frozen foods that are consumed after heating are classified as ``frozen foods that have been manufactured or processed and are not frozen foods that are consumed without heating.'' It is explained as follows.
Whether the food is heated just before freezing or unheated just before freezing depends on the product, but in general, fried foods such as french fries, croquettes, and fried shrimp fall under the category of frozen foods that are consumed after heating.
Reference: Standards for each food (frozen foods) (Osaka Quarantine Station Food Inspection Division)
Unheated frozen food
Frozen food that can be eaten as is without being heated before eating. Specifically, this would include cakes and fruits.
In addition, the definition of frozen food that is consumed without heating does not ask whether the food was heated before thawing. In the end, the types are classified based on whether or not they should be heated before eating.
Frozen seafood for raw consumption
Frozen shelled or filleted fresh seafood that can be eaten raw. Because it is meant to be eaten raw, it is not heated during production, and although it does require thawing when eaten, it does not require heating. For frozen fresh seafood for raw consumption, only those in packaging containers fall under this category.
Typical examples include frozen foods such as sashimi and sushi toppings.
Frozen fresh seafood, filleted or shelled
Frozen shelled or filleted fresh seafood. The difference from the above-mentioned frozen fresh seafood for raw consumption is that it is not intended for raw consumption.
This type falls under the category of frozen foods that are consumed after heating. Therefore, it must be cooked before eating, but it is not heated at the time of manufacture. Specifically, this would apply to seafood that is put in a hot pot.
What rapid freezing, which is essential to the frozen food manufacturing process?
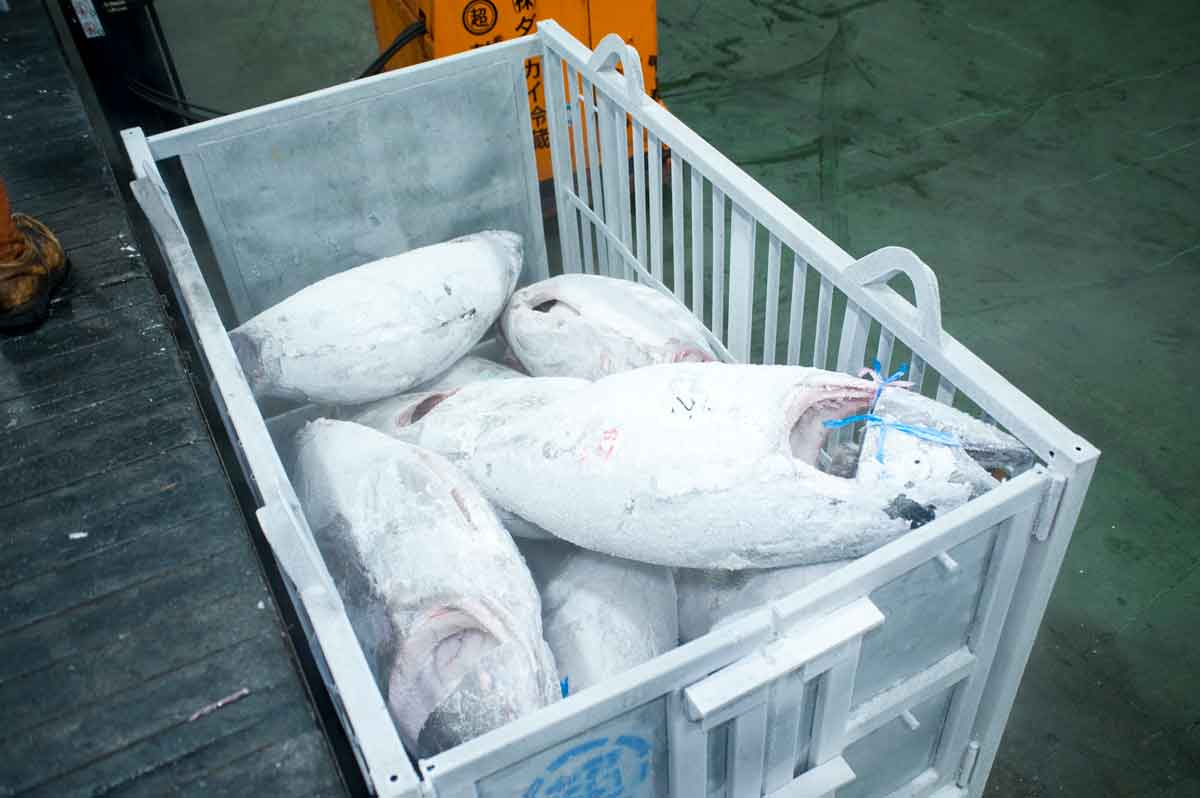

In order to produce frozen foods, the" rapid freezing "equipment that I mentioned earlier is essential. In this chapter, we will explain in detail what rapid freezing is, citing specific benefits.
Why rapid freezing is necessary for frozen foods
For example, when manufacturing and selling specialty dishes and ingredients as frozen foods, it is extremely important not to compromise the taste or quality of the food.
For example, when food and ingredients are slowly frozen using a home freezer, it takes many hours to pass through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature range where ice crystals tend to become coarse, making up 70 to 80% of the food. As water turns into ice, its volume expands, destroying the cells of the food.
Also, if you freeze the food slowly, the umami ingredients and water may leak out from the broken cells, resulting in a loss of flavor and texture.
On the other hand, rapid freezing is a technology that allows food to pass through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature range, where the water in the food turns into ice crystals, within 30 minutes. rapid freezing suppresses the growth of ice crystals, making it difficult for the cellular structure of the food to break down.
As introduced in the four conditions above, the Japan Frozen Foods Association (General Incorporated Association) recommends that companies have a process that allows for rapid freezing in order to manufacture and sell frozen foods of higher quality. I'm looking for it.
Can preserve the original taste and flavor
When food passes through the maximum ice crystal formation temperature range within 30 minutes through rapid freezing, the cells of the food are less likely to break down, making it difficult for the following elements of dishes and ingredients to deteriorate.
- freshness
- Taste
- quality
- Color
- flavor
- texture etc.
When we think of "frozen foods," we tend to think of them as being for home use, but rapid freezing technology is also widely used for commercial purposes, as it makes it easier to maintain the appeal of the foods mentioned above.
Can freeze large amounts of food
By introducing rapid freezing technology, you can compress the time it takes for dishes and ingredients to completely freeze. For example, the results of a survey by the Japan Frozen Foods Association show that there is a difference of more than three times in the time it takes for food to reach -20 degrees Celsius between ordinary freezing methods (slow freezing) and rapid freezing. Masu.
However, the specific time required will of course vary depending on the type of food and the type of freezer used. This cannot be said in general.
However, if rapid freezing system is introduced, the amount of frozen food that can be produced per day can be significantly increased by shortening the freezing time.
Source: Why rapid freezing is good (Japan Frozen Food Association)
Safe in terms of hygiene
It is said that the growth of many bacteria is delayed at temperatures below 10 degrees Celsius, which is the standard temperature inside the refrigerator, and stops at temperatures below -15 degrees Celsius.
If you use rapid freezing technology to freeze dishes and ingredients all at once, you will be able to quickly pass through the temperature range where bacteria stop growing. As a result, food poisoning problems are less likely to occur.
Artlock Freezer is recommended for manufacturing frozen foods.
Daybreak's "Artlock Freezer" is recommended for those who produce high-quality frozen foods.
The feature of Artlock Freezer is that it can rapid freezing food by surrounding it with gentle cold air. Unlike general rapid freezer, this system does not apply strong cold air to the food from one direction, so it minimizes damage to the food and prevents drying, discoloration, and oxidation.
In addition, foods frozen in the Artlock Freezer can be stored for long periods of time, such as six months. Therefore, it is a system suitable for manufacturing frozen foods, as it allows you to store large quantities of food for a long time before shipping.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process for frozen foods is designed based on strict conditions as introduced in the article. Therefore, the general process for manufacturing frozen foods remains basically the same at all factories.
Manufacturers of frozen foods need to manage the entire process, from pre-treatment before freezing to packaging after freezing. Among these, rapid freezing, which has been attracting attention in recent years, can be thought of as a mechanism that is at the core of the frozen food process.
Daybreak, which develops and sells Artlock freezers, provides total consulting related to rapid freezing. If you are interested, please contact us from the page below.








![[Storage period increased by 30 times! ] Achieving a stable supply of raw whitebait!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/579c55e6d32e1385c250e8e7c3ed59a71.jpg)
![[Sales increased 100 times! ] rapid freezing the signature menu “Ni-katsu sandwich”!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/IMG_02391.jpg)
![[Horse sashimi] We have significantly reduced waste loss with rapid freezer!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/5fda59d0cbcdabde18e58c3c58c09ed0.jpg)




![[Storage period increased from 3 days to half a year! ] Restaurants are expanding their business using wholesale and mail order!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/66c19942ab4ba346fdb64ccc04cde373.png)
![[Reduce loss from 200 kg of oysters to zero] Improve loss and expand business with rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/19785ca583a8d3c4041c7c192d041b0d.jpg)















![Introducing recipes and methods for freezing spinach [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/spinachh-768x512-1.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze green beans, storage period, and 5 recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/f3dbbe5b1d05a50f514a833efdceced9.jpg)
![Explaining how to freeze garland chrysanthemums with photos! [Defrosting and storage period, 5 recipes]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/syungiku-catch-768x512-1.jpg)
![[Fruit becomes dessert! ] How to freeze kiwi and sweets recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ecc0fc2bc14391ea13ce2e7a43d1416e.jpg)
![[Delicious frozen foods] How to use them in lunch boxes, dinners, and snacks](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/frozen-food-1024x683-1.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze hijiki and its storage period, 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ff6bdc527dd066b7d725a48161d7925d.jpg)
![How to freeze natto, expiration date, baby food and carefully selected recipes [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/055e5e865986b68d11c3f49f11ea6008.jpg)
![[Mass production and space saving] What is the secret of the spiral freezer structure?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/3d-sp.jpg)

![[Is it more nutritious than raw? ] Introducing recipes and how to preserve frozen blueberries](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/bdc074d8bfa2dc63c2c7bf92dc1dd07d.jpg)
![How to freeze rice cake, expiry date, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/bd019f04ad570f697ffefe9ffd2e1e71.jpg)





![[Commercial use] Thoroughly investigate the cause of frost forming in the freezer! How to prevent frost formation?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/09c17e4deeb1ac0cdc5a513eaf89ab1a.jpg)


![[Wholesale] Advantages and success stories of introducing rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/jirei_oroshi_img_01.jpg)




![Types of rapid freezer and purchasing points! [Examples of failures in machine selection! ? ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/e68b2ac878e110c2a4639a33271057d1_s-1.jpg)
![[Delicious food] Solving nursing home management issues with freezing and cooling technology](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/7cabe275da8be8736f4496b952bde332.jpg)


![[Advantages and disadvantages of food additives] What is rapid freezer that solves the problems?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/ea1a552f8cb49685b3566dc4f06cf04b.webp)
![[Deliver delicious ham! ] Meat processing manufacturer’s rapid freezing implementation example](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/0825c4a97ac8495fd2408a91574cede6.jpg)
![[For food manufacturers] What is the meaning of IQF freezing and what is rapid freezer required for it?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/40008d9f1a752dd006399fe1c4beda34.jpg)
![[Be good at saving money! ] Introducing the method and recipe for freezing fried rice](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/mayo-tyahan-1024x768-1.jpg)
![[Thorough Guide to Preserving Sweets] Introducing the freezing method, storage period, and thawing method in detail!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/bffcbc0b6e79bb1af6e05b930e11e949.jpg)
![How to freeze apples and what is their nutritional value? Perfect for baby food! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/cf0380a4b371d2f43e0f0ed99c7344a2.jpg)
![How to freeze and thaw chestnuts, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/c590a9e6fb16ed45fe2fdd32813de03b.jpg)
![[Lunch boxes are easy! ] Techniques and recipes for effectively using frozen side dishes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/reitou-bento-1024x682-1.jpg)
![[Nutrition remains the same! ? ] Introducing how to use frozen vegetables and recommended recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/vegetables-reito-1-1-768x511-1.jpg)
![Freezing garlic, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/30693b4b122ff6c57afff367b35bc861.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze pork, expiration date, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/8688cd28f298c3180c30169cec815293.jpg)
![[Can it be frozen? ] Introducing a good way to freeze green peppers and side dish recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/30407f106c5c082468c66af0d40c5858.jpg)
![How to freeze chicken, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/01f6582931e13522ee0d1ee900be2d1d.jpg)
![[Recover the machine cost in about 1 year! ]Reduce loss of tiger puffer fish with rapid freezing!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/1772bacb83f79fbd476ca3d66c8f8281_s1.jpg)
![Introducing how to freeze/thaw salmon roe and how long to store it [includes carefully selected recipes]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/236b884b68d07d2f5983f2b9ea66583d.jpg)

![[Make frozen oysters even more delicious! ] Correct thawing method and usage recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/5855c6e6d6dbdb298f86405b4b522329.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze taro, storage period, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/116858380_-768x512-1.jpg)
![[Import/Export Industry] Advantages and success stories of introducing rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/jirei_yunyu_img_01.jpg)



![[Must-see for bakers] 6 reasons why bakeries should use rapid freezing](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/f92a102c9d3cc8c63dc7e509ce6d35d2.jpg)











