How much does disposal loss cost? Introducing measures to reduce food loss

Do you know how much it costs to dispose of food waste?
Food waste occurs when food that is still edible, such as leftovers or unsold items, is thrown away (food loss). When food is thrown away, the materials and labor used in its production are wasted, and in addition to contributing to environmental degradation and food insecurity, it also causes economic losses due to disposal.
For this reason, efforts are being made to reduce food waste and loss in countries around the world, and Japan is no exception.
In this article, we will explain the causes and economic losses of waste loss, as well as introduce specific efforts to reduce waste loss.
目次
What is food waste loss?
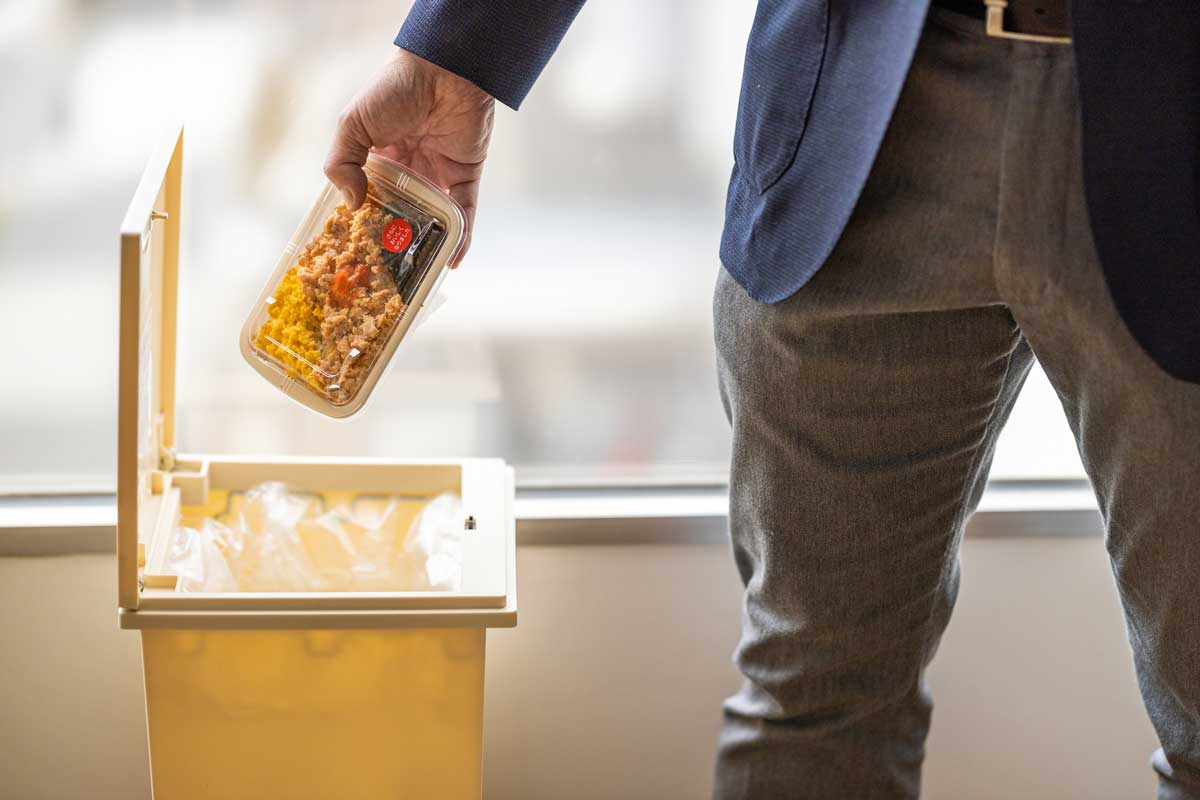

First, I will explain food waste loss.
Losses when food is thrown away
Waste loss refers to the loss caused by discarding food that is otherwise edible. When referring to the food itself that is discarded, it is called "food loss."
In Japan, 5.23 million tons of food waste is generated annually, of which 2.79 million tons are business-related food loss and 2.44 million tons are household food loss. When converted to per capita, this means that approximately 42 kg of food is lost per year.
By the way, what about the world as a whole? According to a survey by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAQ), the amount of food wasted is 1.3 billion tons per year, and it is estimated that one third of the food produced for human consumption is subject to waste..
Food waste not only leads to environmental degradation and food crises, but also causes serious economic losses. There are two types of disposal losses in companies: "costs incurred in purchasing or production" and "costs incurred in disposal."
Efforts are needed to reduce food waste and loss in order to reduce the economic losses caused by food waste.
Causes of waste loss
Food waste also occurs when edible food is thrown away, that is, food loss.
There are two main causes of food loss in Japan. One type is business-related food loss, which includes returns and unsold items at retail stores such as convenience stores and supermarkets, and leftover food at restaurants.
Another issue is household food waste. In addition to leftovers due to over-cooking, there are also foods that are thrown away without being eaten due to expiration dates (direct disposal), and foods that are peeled too much (over-removal).
In order to reduce waste loss, it is important for each and every citizen to be aware of this.
How much does waste loss cost?
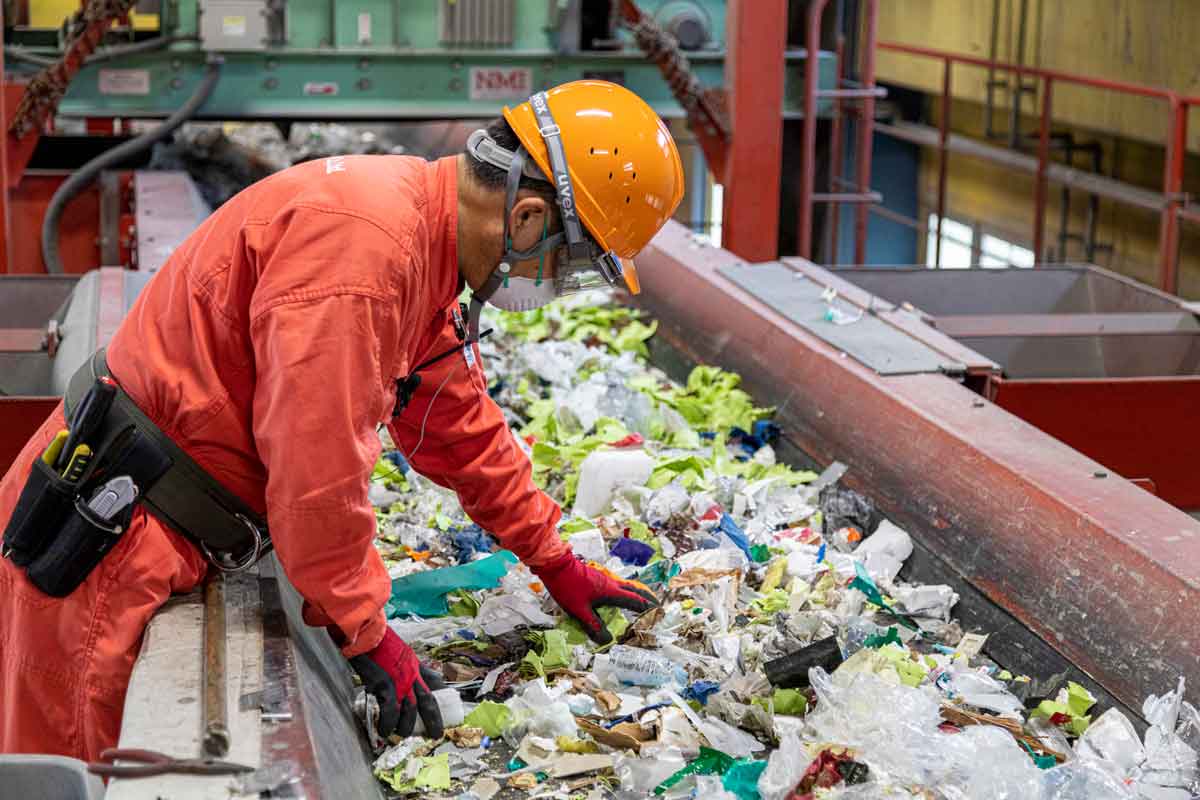

How much is the economic loss caused by disposal loss? Let's take a closer look, focusing on the cost of waste disposal.
Waste disposal costs
Waste is broadly divided into general waste and industrial waste. Industrial waste refers to 20 specific types of waste generated by business activities, and the rest is treated as general waste. The handling of general waste differs depending on each municipality, but examples include combustible garbage, non-burnable garbage, bulky garbage, home appliances, bicycles, computers, hazardous garbage, human waste, etc.
When it comes to food, the waste generated during the production stage by food manufacturers is considered industrial waste, but all the waste generated during the distribution stage at supermarkets, department stores, restaurants, etc., including food loss, is classified as general waste.
According to an announcement by the Ministry of the Environment, the cost of processing general waste in fiscal year 2021 is 2,144.9 billion yen. Regarding the breakdown of general waste, referring to the 2008 Fukui City survey, 82% of the garbage generated in Fukui City is combustible garbage, of which 46% is food waste. is.
Let's calculate this by assuming that the percentage is roughly the same for other cities, wards, towns and villages.
2,144.9 billion x 0.82 x 0.46 = 809 billion
In other words, 809 billion yen is spent annually on food waste.
Annual cost per capita
If you divide the cost of food waste (approximately 809 billion yen) by the number of people, it means that each person costs approximately 6,500 yen per year.
Furthermore, how much of the food waste is lost due to food that is considered edible? As an example, of the 24.02 million tons of food waste in FY2021, food loss accounted for 5.23 million tons, or about 22%. Let's apply this to the amount per person.
6,500 yen x 0.22 = 1,430 yen
In other words, each person costs us 1,430 yen per year to throw away edible food.
In addition, waste loss includes not only garbage disposal costs, but also the procurement, production, and purchase costs of ingredients. For example, a survey of ordinary households in Kyoto City found that waste loss, including the purchase cost of uneaten food, came out to be 60,000 yen per household per year.
Reference: Kyoto City food waste data | Kyoto City Zero Food Loss Project (sukkiri-kyoto.com)
Three ways to reduce waste loss

In order to reduce food waste and reduce waste loss, it is important for each and every citizen to be aware of this.
The core of our efforts to reduce waste loss is the 3Rs. The 3Rs are an acronym for "Reduce, Reuse, Recycle," and were originally created as an approach to environmental issues.
Let's apply these 3Rs to food waste and think about it specifically.
Reduce (REDUCE)
"Reduce" has the meaning of "suppression of generation," and the idea is to suppress the generation of waste loss itself. Reduction is the shortest way to reduce food loss and waste.
Below are some concrete examples that you can put into practice starting today.
- When shopping, buy only the amount of ingredients you can use by selling them individually or by weight.
- When eating out, order the appropriate amount to avoid leftovers.
- Try to preserve purchased ingredients by pre-processing them and freezing them.
- Enjoy delicious cooking methods such as the head of fish and the skin of vegetables.
Recently, an increasing number of local governments are calling for "temaedori" (temaedori). This is an initiative to encourage people to buy products with the closest expiry date or use-by date when purchasing ready-to-eat foods at supermarkets or convenience stores.
Reuse (REUSE)
Reuse means "recirculation." This refers to putting food back into circulation by devising food sales methods or donating surplus food.
Let's introduce some specific initiatives.
- Sell foods that are expired, close to expiration date, out of season, etc. at a lower price.
- Donate food that would otherwise go to waste to people in need through food banks and food drives
By the way, the difference between a food bank and a food drive is that the former collects donations primarily from businesses that handle food, while the latter collects donations from households that have bought too much food. The collected food will be delivered to organizations and welfare facilities that support people in need.
Recycling (RECYCLE)
Recycling has the meaning of "reproduction" and is an effort to reduce the amount of garbage by turning discarded food into resources.
- Reusing food residue (food-derived waste from food-related businesses) to make feed for livestock (Ecofeed)
- Food residue is rotten by microorganisms and turned into compost or fertilizer.
- Methane fermentation of food waste to produce methane gas and reuse it as energy
- Generate electricity by using the heat generated when trash is incinerated
What is rapid freezer that is effective in reducing waste loss?
The use of rapid freezer has recently been attracting attention as a measure against food loss and waste.
rapid freezer is a technology that allows food to be frozen and thawed without sacrificing quality by freezing the food without destroying its cells.
Conventional freezing results in quality deterioration such as drips, discoloration, and odors, but by using rapid freezing technology, it is now possible to freeze foods that could not be frozen in the past without losing quality.
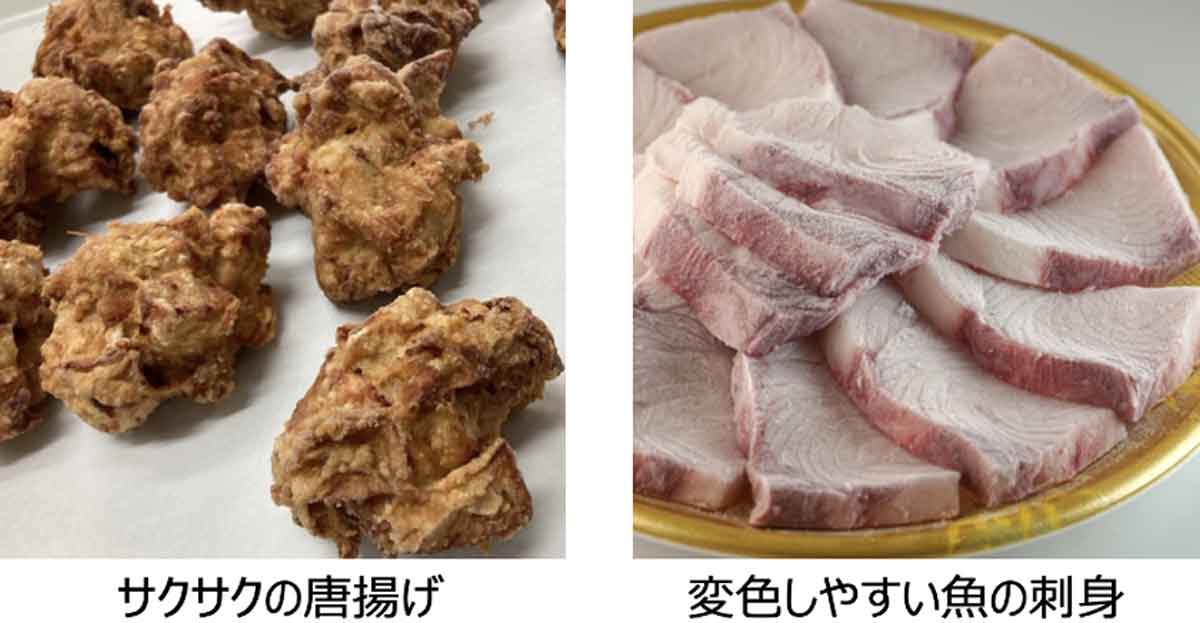

rapid freezing allows for long-term storage without compromising quality, eliminating the causes of waste loss that previously occurred.
- Eliminate waste caused by over-purchasing by storing ingredients frozen and thawing only the amount you need.
- By freezing excess harvested food, you can eat it when you need it without wasting it.
- Avoid waste by freezing overcooked food
By using rapid freezer, we are able to reduce the amount of food waste that occurs in a variety of situations. Therefore, it is used by a variety of companies, from restaurants to food manufacturers.
Conclusion
As we have introduced so far, 5.23 million tons of food loss occurs annually, of which 2.79 million tons are business-related food losses and 2.44 million tons are household food losses. Additionally, wasting edible food results in large economic losses.
A new method to eliminate this waste loss is the use of rapid freezer. Since it can be stored for a long time without compromising quality, it is attracting a lot of attention as a measure to reduce waste loss.
If you want to reduce waste loss, please consider using rapid freezer.








![[Storage period increased by 30 times! ] Achieving a stable supply of raw whitebait!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/579c55e6d32e1385c250e8e7c3ed59a71.jpg)
![[Sales increased 100 times! ] rapid freezing the signature menu “Ni-katsu sandwich”!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/IMG_02391.jpg)
![[Horse sashimi] We have significantly reduced waste loss with rapid freezer!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/5fda59d0cbcdabde18e58c3c58c09ed0.jpg)




![[Storage period increased from 3 days to half a year! ] Restaurants are expanding their business using wholesale and mail order!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/66c19942ab4ba346fdb64ccc04cde373.png)
![[Reduce loss from 200 kg of oysters to zero] Improve loss and expand business with rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/19785ca583a8d3c4041c7c192d041b0d.jpg)






















![How to freeze tomatoes, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/tomato-768x513-1.jpg)


![[Explanation with photos] How to freeze winter melon, storage period, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/8c301e3fcfbb9c7f457d8b05dfea902d.jpg)
![Explaining how to freeze garland chrysanthemums with photos! [Defrosting and storage period, 5 recipes]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/syungiku-catch-768x512-1.jpg)
![How to freeze potatoes and a great time-saving recipe! [Moms must see! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/potato1-768x512-1.jpg)

![Introducing how to freeze burdock and recipes [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/0812c28da547fe267723143edad2bfed.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze mackerel fillets and 5 carefully selected recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/bf45f102162a8d43387d3a8d3e538034.jpg)
![How to freeze cucumbers and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/37a83e91a989dfbc285ac11dede7c8c2.jpg)
![[Includes recommendations by industry] Summary of types and benefits of small rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smallsize.jpg)
![[Can it be frozen? ] How to freeze fresh cream, storage period, thawing method and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/1887f5bd8f2d7f9ef1d88754f2c5bcc4.jpg)


![Freezing garlic, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/30693b4b122ff6c57afff367b35bc861.jpg)

![[Freezing Neapolitan] rapid freezing demonstration](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/napolitan.jpg)




![[Labor shortage]The benefits with examples of using rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/hitodebusoku-article-main_pc.jpg)

![[Explanation with photos! ] Shiitake mushroom freezing method and storage period, 5 recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/shiitake-768x512-1.jpg)

![[Fisheries/Fisheries Cooperative] Advantages and success stories of introducing rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/jirei_suisan_img_01.jpg)
![How to freeze rice cake, expiry date, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/bd019f04ad570f697ffefe9ffd2e1e71.jpg)
![How to freeze sweet potatoes, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/36256af24531b73a036523ba73bdf9ec.jpg)

![[Used and energy-saving types also available] Points to keep in mind when using refrigerated/frozen showcases](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/9a1f5615c9649610709c0e4a29df5f57.jpg)
![[Required for Cook Chill System] How much does a blast chiller cost?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/fc29ddca3d7d1f8d53bf99518ce28fcf.jpg)

![[Commercial rapid freezer] Explaining the features, size, and price of Panasonic rapid freezing](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/panasonic.jpg)
![[Advantages and disadvantages of food additives] What is rapid freezer that solves the problems?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/ea1a552f8cb49685b3566dc4f06cf04b.webp)
![[Thorough guide to preserving meat] Preservation methods, expiration dates, thawing methods, rapid freezing](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ec61889773cfed9c75aa97d9ca6c96dd-1.jpg)


![[Bringing fresh cakes nationwide] How to dramatically increase profits at a pastry shop?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/661ea3ee6264fab6520017622c656870.jpg)

![[Convenient for lunch boxes! ] How to freeze fried noodles and 5 different recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/yakisoba-768x512-1.jpg)

![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze pumpkin, storage period, and 5 recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/36d3edf3acec7cf27351bd1211e770ac.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze taro, storage period, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/116858380_-768x512-1.jpg)
![[Be good at saving money! ] Introducing the method and recipe for freezing fried rice](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/mayo-tyahan-1024x768-1.jpg)



![[Introducing case studies as well!] 5 reasons why curry restaurants should install rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/2a0deb9a6db53165f0a4938bc80cee46.jpg)
![[Freezing dried persimmons] rapid freezing demonstration](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/cc45cd14917f372d2e7aa6a5eeda4583.webp)
![Introducing how to freeze and thaw whitebait, as well as recipes for its use [Full of nutrition! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/04d15012ec36f91a5574f63dfa9d4771.jpg)



![[Food/processing manufacturers] Advantages and success stories of introducing rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/jirei_kakou_img_01.jpg)
![How to freeze/thaw turnips, storage period, and 5 recipes [Explanation with photos]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/eae0789d04cc4971cf4232963b4d2231-1.jpg)

![[Can it be frozen? ] How to freeze milk, storage period, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/d0390cbc7a5e9a76c11d5b9eff3b4a5b.jpg)
![[Required for food business operators] What is the reason for implementing HACCP and using rapid freezing?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/b9dcd4b8ff706013bae4aafeda989b6e.jpg)



![[Manufacturing subsidies are recommended for rapid freezer! ] Explaining the ABCs of application](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/4024568_s.jpg)
![[Eliminating the labor shortage! ] Introducing the benefits of the cook-freeze system!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/95e9f56fecc5fd995cb205bd5b13596c_s.jpg)





