What causes food poisoning? ? About the types and foods that are likely to cause them

It is necessary to take appropriate measures depending on the cause of food poisoning, and incorrect knowledge can lead to serious food poisoning.
This time, we will introduce the causes of food poisoning and the foods that are likely to be the source of infection. Get the correct knowledge and prevent food poisoning from occurring.
目次
What is food poisoning?

Food poisoning is a poisonous disease caused by food, such as gastroenteritis or neurological disorders, which often causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. Also, food poisoning does not include food poisoning caused by food allergies.
There are many different types of food poisoning that can cause food poisoning. Let's take a look at what's available.
Causes of food poisoning
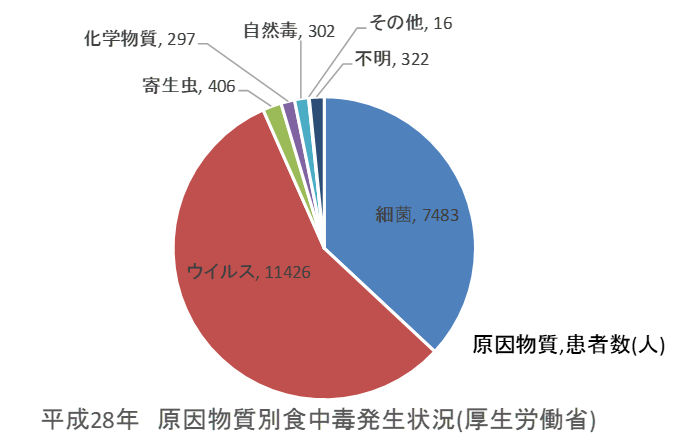
Substances that are thought to cause food poisoning include those that are originally present in food and those that adhere to food and reproduce there. The causes are broadly classified into five categories.
In 2016, there were 20,252 food poisoning patients, and the causative agents were as follows.
bacteria
Bacteria are small, invisible creatures that multiply in food depending on conditions such as temperature and humidity. Bacteria breed particularly easily during the high temperatures from June to September, and food poisoning occurs frequently. Bacteria that can easily cause food poisoning include:
-
- Staphylococcus aureus
-
- Clostridium botulinum
-
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
-
- Salmonella spp.
-
- campylobacter
-
- Pathogenic E. coli
- Clostridium perfringens
There are many other bacteria that can cause food poisoning. Among them, food poisoning caused by Campylobacter and Clostridium perfringens occurs frequently.
Campylobacter is a bacterium that naturally exists in cows, pigs, chickens, etc., and eating raw meat increases the risk of contracting it. It can also occur with liver sashimi, chicken sashimi, and milk. Clostridium perfringens is a bacterium that lives in water and soil, and multiplies in foods that are cooked in bulk, such as curry and stew.
virus
Viruses are smaller than bacteria and can enter the cells of humans and animals and multiply. The difference is that bacteria can divide and reproduce on their own, whereas viruses cannot reproduce on their own.
The most common type of food poisoning caused by a virus is "norovirus," which occurs all year round, regardless of the season. Norovirus multiplies in the human intestine and can cause infection even in small amounts. People may engage in cooking without realizing that they have been infected with norovirus, and the infection may spread.
parasite
Food poisoning is caused by insects that live in fish, meat, water, etc.
The most common cause is "Anisakis," which is a parasite that infects salmon and mackerel. Since Anisakis does not grow inside the body, it is usually excreted over time, but it can invade the stomach and intestinal walls and cause severe abdominal pain.
natural poison
Food poisoning is caused by toxic ingredients naturally present in animals and plants. Natural toxins include ``solanine'' contained in potatoes and poisonous mushrooms, ``tetrodotoxin'' contained in blowfish, and shellfish poison. In addition to symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea, symptoms include numbness, difficulty walking, and paralysis.
Chemical substance
Food poisoning can also be caused by harmful chemicals that are not naturally present in food. Most cases are caused by histamine, which is caused by eating red-fleshed fish such as bonito, tuna, and mackerel. Red-fleshed fish such as bonito contain a lot of a substance called histidine.
This histidine is converted to histamine by histamine-producing bacteria, and the increased amount of histamine causes food poisoning. Once formed, histamine cannot be decomposed by heating and can proliferate even at low temperatures, so care must be taken.
Also, detergents and bleaches can be mistaken for seasonings, so if detergents are refilled in plastic bottles, etc., be sure to clearly label them so food preparation staff can understand. Please do not place it nearby.
The cause of food poisoning is often unclear. If you operate a school lunch facility or produce prepared foods, this may be because you handle a large number of ingredients, or the same food is manufactured at multiple facilities.
In addition, food poisoning caused by viruses may not be directly caused by food, and it may be difficult to identify the source of infection.
Food poisoning by food

There are many other causes of food poisoning other than those listed above. Also, the causes of food poisoning vary depending on the food. Let's take a look at the causes and characteristics of food poisoning.
Rice/spaghetti
●Fried rice, pilaf, spaghetti
[Cause] Bacillus cereus
[Characteristics] This is likely to occur if cooked food is left at room temperature for a long period of time.
Bacillus cereus forms heat-resistant spores (does not die even after heating at 100℃ for 30 minutes)
[Countermeasure] Cook only the amount you need, and store it in the refrigerator or insulated cabinet when not using it right away.
●Rice ball
[Cause] Staphylococcus aureus
[Characteristics] It widely inhabits wounds, noses, throats, and skin of humans and animals, and even healthy people may carry it.
Generates a heat-resistant toxin called enterotoxin (does not decompose even after heating at 100℃ for 20 minutes)
[Countermeasures] Avoid cooking with bare hands and use plastic wrap or disposable gloves.
meat
●Beef
[Causes] Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and Campylobacter
[Characteristics] Even a small amount of enterohemorrhagic E. coli can cause food poisoning. Children and the elderly are more likely to become seriously ill, with some cases of death.
[Countermeasure] Heat thoroughly when cooking. Avoid raw food.
Beef liver cannot be served raw.
●Pork
[Causes] Parasites, hepatitis E virus, salmonella bacteria
[Characteristics] The parasite (Toxoplasma) found in pigs affects the fetus if infected during pregnancy.
[Countermeasure] Heat thoroughly when cooking. Avoid raw food.
Pork liver cannot be served raw.
●Chicken
[Causes] Salmonella, Campylobacter
[Characteristics] Salmonella bacteria are often found in eggs.
[Countermeasure] Heat thoroughly when cooking. Avoid eating raw eggs and meat. Do not crack the eggs.
●Wild animals such as deer, boars, bears, etc.
[Causes] Parasites, hepatitis E virus
[Countermeasure] Heat thoroughly when cooking. I don't eat it raw.
fish
●Saltwater fish, shellfish, seaweed
[Cause] Vibrio parahaemolyticus
[Characteristics] Vibrio parahaemolyticus prefers seawater and grows rapidly.
[Countermeasure] Wash thoroughly with fresh water when cooking. Store at low temperature.
●Squid, mackerel, saury, flounder, etc.
[Cause] Parasites (Anisakis, Kudoa)
[Characteristics] Kudoa is parasitic on flounder.
It is sensitive to heat and will die if frozen for a long time.
[Countermeasures] If eating raw, freeze at -20℃ for at least 24 hours.
⇒⇒⇒ [Safely distribute delicious fish! ] Kill Anisakis with rapid freezing technology!
vegetables
●Raw vegetables and pickled vegetables
[Causes] Bacteria found in the soil such as enterohemorrhagic E. coli, Salmonella enterica, Bacillus cereus, and Listeria monocytogenes
[Countermeasures] When eating vegetables raw, sterilize them using sodium hypochlorite solution, electrolyzed water, ozonated water, etc.
Stews
●Curry, soup, meat and potatoes, etc.
[Cause] Clostridium perfringens
[Characteristics] Clostridium perfringens prefers places with little oxygen.
It grows near the bottom of pots of foods that are cooked in large quantities, such as curry.
[Countermeasures] If you are not going to serve the food immediately after cooking, cool it immediately and store it.
vacuum packed food
●Packed cooked products
[Cause] Clostridium botulinum
[Characteristics] Clostridium botulinum grows in conditions with little oxygen.
[Countermeasures] Store at below 10℃. Or heat at a high temperature of 120℃ for 4 minutes or more.
It should be clearly stated that foods that have not been sterilized by high-temperature heating should be stored in the refrigerator so that consumers do not make the mistake.
Conclusion
What did you think. Food poisoning can be caused by many different things.
In order to avoid food poisoning, it is necessary to always be aware of the types of foods that can cause food poisoning and the types of foods that are likely to cause food poisoning when handling food.
All staff involved in cooking should learn how to prevent food poisoning and prevent food poisoning.
⇒⇒What are the three principles for food poisoning prevention? What to do to avoid food poisoning
⇒⇒ Avoid the risk of food poisoning with rapid freezing! [Introduction record of rapid freezer]








![[Storage period increased by 30 times! ] Achieving a stable supply of raw whitebait!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/579c55e6d32e1385c250e8e7c3ed59a71.jpg)
![[Sales increased 100 times! ] rapid freezing the signature menu “Ni-katsu sandwich”!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/IMG_02391.jpg)
![[Horse sashimi] We have significantly reduced waste loss with rapid freezer!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/5fda59d0cbcdabde18e58c3c58c09ed0.jpg)




![[Storage period increased from 3 days to half a year! ] Restaurants are expanding their business using wholesale and mail order!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/66c19942ab4ba346fdb64ccc04cde373.png)
![[Reduce loss from 200 kg of oysters to zero] Improve loss and expand business with rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/19785ca583a8d3c4041c7c192d041b0d.jpg)














![[For vegetable processors] What is the blanching process that improves the quality of frozen vegetables?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/ad38a1a4c704bc39303ac1864f5b0b8d.jpg)
![[Safely distribute delicious fish! ] Kill Anisakis with rapid freezing technology!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/99093c5fe8b0d716c39df907616e4a96.jpg)
![[Delicious frozen squid recipe! ] Tips on how to eat squid deliciously and without waste](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/f3bc339b6bcaff01bd8e2aaa4257acfe.jpg)
![Anisakis that won't die can be killed by freezing! [Appropriate freezing prevention for food poisoning]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/c5dabe6d1921ee78ce0b63f14cc56a4c.jpg)


![[8 times more nutrition! ] Introducing how to freeze clams, storage period, and 5 recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/57204e2a2f115f810e29e365cfc86638.jpg)
![[How long does it last? ] How to freeze cooked rice and how long it can be stored](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/7e31499b015d58f220536e3274a41bf2.jpg)
![[Many repeat customers! ] Increase sales by mail ordering our proud curry by rapid freezing!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/S__295895302-863x10241.jpg)
![[Lunch boxes are easy! ] Techniques and recipes for effectively using frozen side dishes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/reitou-bento-1024x682-1.jpg)
![[A must-see for restaurants that serve rice] What is rapid freezing that can preserve rice for a long time?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/rice.jpg)
![[Be good at saving money! ] Introducing the method and recipe for freezing fried rice](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/mayo-tyahan-1024x768-1.jpg)
![[Recommended for those living alone! ] How to freeze rice, storage period, and easy recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/b3c2c946949856ed2c8a8098eacf6641.jpg)
![[Convenient for lunch boxes! ] How to freeze fried noodles and 5 different recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/yakisoba-768x512-1.jpg)
![[Shop for carefully selected fresh udon] 5 reasons why udon restaurants should introduce rapid freezing](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/713146fd51058df15ccc18c6188c1407.jpg)


![[Freshly made raw soba all over the country! ] Example of introducing a quick freezer at a soba restaurant](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/6d8138adcf26c410c11b25d5b8d2f3de.jpg)
![[Increase sales! ] Three reasons why ramen restaurants should install rapid freezer](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/ra-men-reitou.jpg)
![[A little different! ? ] How to defrost frozen udon and 7 different recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/91fb1e27ec38400acc9b3b6ca6233f65.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos] How to freeze winter melon, storage period, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/8c301e3fcfbb9c7f457d8b05dfea902d.jpg)
![[Freezing boiled food] rapid freezing demo](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/4739208abfe6e2e63a43347c1598e991.webp)



![How to freeze potatoes and a great time-saving recipe! [Moms must see! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/potato1-768x512-1.jpg)
![How to freeze sweet potatoes, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/36256af24531b73a036523ba73bdf9ec.jpg)

![Freezing garlic, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/30693b4b122ff6c57afff367b35bc861.jpg)
![[Can it be frozen? ] Introducing a good way to freeze green peppers and side dish recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/30407f106c5c082468c66af0d40c5858.jpg)

![Explaining how to freeze Maitake mushrooms, their nutritional value, and recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/9face03809f7fcaf2e3599773b2e8c80.jpg)
![Introducing recipes and methods for good frozen preservation of okra [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/616c25d6c59f80c7a09effe2edc5ef92.jpg)
![[Freezing Neapolitan] rapid freezing demonstration](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/napolitan.jpg)




![[Must-see for bakers] 6 reasons why bakeries should use rapid freezing](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/f92a102c9d3cc8c63dc7e509ce6d35d2.jpg)

![[Bringing fresh cakes nationwide] How to dramatically increase profits at a pastry shop?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/661ea3ee6264fab6520017622c656870.jpg)


![Shock freezer prices and reasons why we can't recommend used ones [What's the difference from a blast chiller? ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/f76c6907f41d0b092e20d0924e5f27c9.webp)

![[Long-lasting freshness! ] Explaining the advantages and disadvantages of chilled storage and chilled transportation](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/64b437bd976e4ef73a85dbb64cdf9fc8.jpg)
![[Used and energy-saving types also available] Points to keep in mind when using refrigerated/frozen showcases](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/9a1f5615c9649610709c0e4a29df5f57.jpg)
![[Advantages and disadvantages of food additives] What is rapid freezer that solves the problems?](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/ea1a552f8cb49685b3566dc4f06cf04b.webp)






![[Nutrition remains the same! ? ] Introducing how to use frozen vegetables and recommended recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/vegetables-reito-1-1-768x511-1.jpg)
![[Can it be frozen? ] How to freeze konjac and diet recipes](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ec03b3e5cdefedf8f295de7ebb781752.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] Introducing the method and recipe for freezing komatsuna](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/5d2a19a6e6cfb5ad0329d8fce162f292.jpg)
![[With photos] Lemon freezing and storage period, recipes for how to use frozen lemons](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/21a01b705aff194717e200bf6dc6ce5b.jpg)
![[Explanation with photos! ] How to freeze taro, storage period, and 5 recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/116858380_-768x512-1.jpg)
![How to freeze mushroom mushrooms, storage period, and 5 recipes! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/4b6ffe2ef040e90085b4ee4f0c3e72a9.jpg)
![How to freeze apples and what is their nutritional value? Perfect for baby food! [Explanation with photos! ]](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/cf0380a4b371d2f43e0f0ed99c7344a2.jpg)
![[Should be frozen! ? ] How to freeze and thaw bread, 5 carefully selected recipes!](https://shunkashutou.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/4691acc32cab80284fa0cddf72d58e95.jpg)













